Early blight is a fungal illness that objectives tomatoes specifically but additionally hits potatoes, peppers, and eggplant.
Early blight can infect vegetation at nearly any time throughout the rising season. It’s maximum prevalent in areas the place there’s top humidity and when temperatures are more than 75°F.
Fungal spores wearing the illness are unfold at the wind or through bugs. Spores germinate and develop when vegetation are wet from heavy dew or common rain.
Goal Crops: Potato, tomato, eggplant, pepper, weeds within the tomato or nightshade circle of relatives.
Explicit Harm:
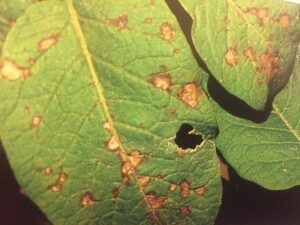
Leaves: signs seem first on older, mature leaves close to the bottom of the plant–one or two abnormal spots in step with leaf, spots ¼ to ½ inch in diameter; spots have tan facilities with concentric ridged rings and yellow halos across the edges, target-shape look with outlined border; spots amplify and coalesce. Massive portion of leaf turns into a diffuse yellow and would possibly drop. No mildew seems. Illness spreads slowly.
Stems: darkish, sunken lesions at or above the soil line, often referred to as collar rot.
End result of tomato, eggplant, pepper: sunken spots seem at the stem finish of culmination; concentric ring trend or target-shape look round spots; illness strikes from stem to rot fruit.
Tubers of potatoes: tuber lesions are brown or black sunken spots not up to ½ inch vast.
How Unfold: Early blight fungi spores are wind- and rain-borne. Once in a while the illness will also be transmitted through flea beetles who‘ve consumed diseased vegetation. Hyphae input the plant thru cracks and wounds in plant tissue.
Existence Cycle: Fungi overwinter on decomposed plant particles and shape new spores each and every spring. A number of generations of spores can happen throughout summer time when the illness is vast unfold.
Natural Keep watch over and Prevention:
- Use seed potatoes qualified illness unfastened.
- Plant resistant types; long-season potato types are maximum resistant.
- Don’t plant tomatoes and potatoes shut in combination to stop go an infection.
- Rotate tomato and potato plants that don’t get early blight.
- Steer clear of overhead watering.
- House and skinny to permit mild and air to succeed in vegetation.
- House potatoes extensively.
- Stake or cage tomatoes, eggplants, and peppers.
- Stay vegetation wholesome; side-dress vegetation with a balanced fertilizer.
- Take away inflamed leaves from vegetation once you notice them.
- Mulch round vegetation to stop fungal spores from splashing onto vegetation.
- Spray vegetation with compost tea or Bacillus subtilis to stop blight from spreading.
- Stay lawn freed from dropped or diseased plant subject matter throughout the rising season.
- Blank lawn of all plant particles on the finish of the season.
- Get rid of tomato circle of relatives weeds comparable to black nightshade that may harbor fungal spores.
Non-Natural Keep watch over: Drench soil with Trichoderma harzianum at planting time. Spray with fungicide containing chlorothalonil. Seek the advice of your close by cooperative extension for regionally-approved fungicides.
Illness Vary: United States and Canada; serious in humid areas, Midwest, humid japanese states.
Clinical identify: Alternaria solani
Prevention of Fungal Sicknesses:
- Take away diseased go away once they seem.
- Fortify air movement round vegetation.
- Mulch across the base of vegetation to cut back water splashing.
- Don’t use overhead watering.
- Keep watch over weeds.
- Rotate plants.








