Would perhaps is the month to get your summer season vegetable garden planted and emerging. Just about all warm-season vegetation can each be sown or transplanted into the garden thru mid-Would perhaps. If you happen to live in a short lived emerging season house (Zones 3 to 6) keep crop protecting devices paying homage to row covers and plastic hoop tunnels and row covers at the in a position.
You’ll want to harden off seedlings started indoors previous than transplanting them out. Make certain the soil stays merely rainy–not wet–until the roots of your vegetation are effectively established. Keep weeds at bay specifically early inside the season; they’re going to be competing for the same nutrients and moisture your more youthful vegetables and herbs need.
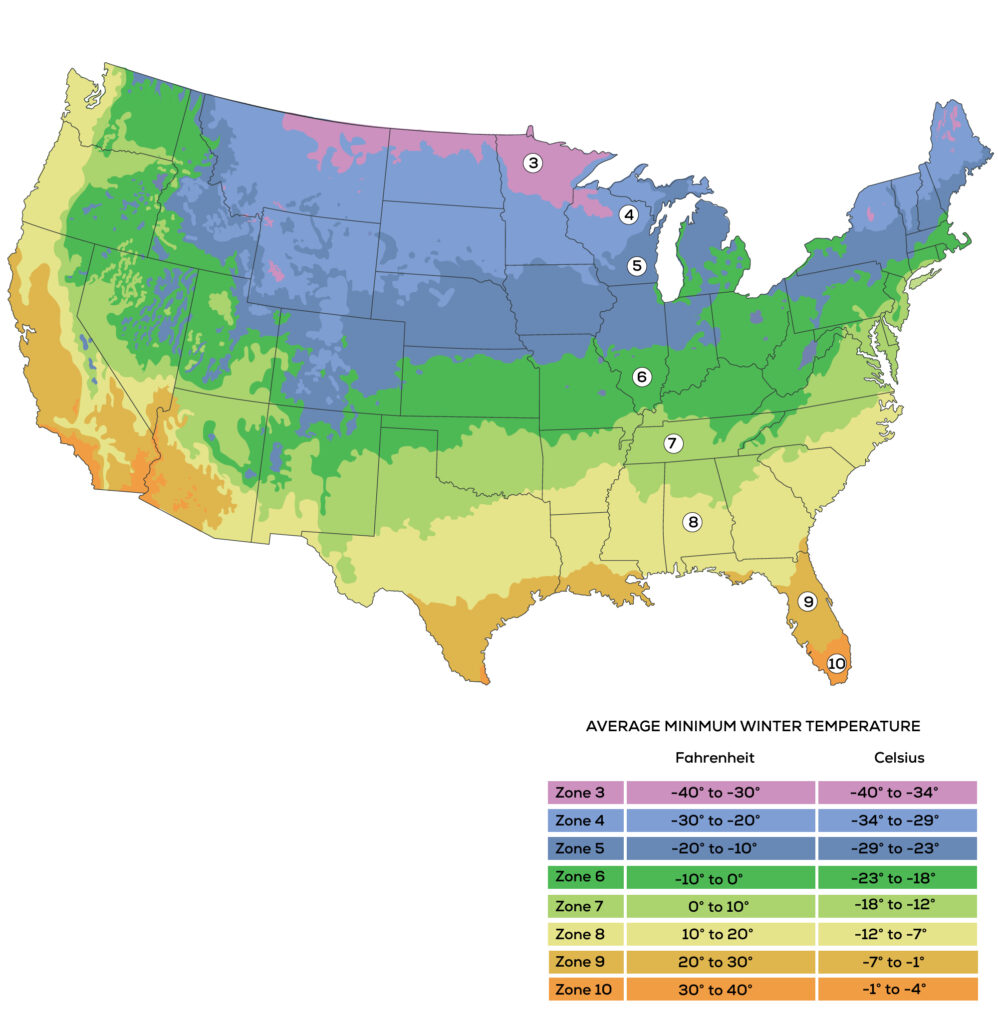
Zone Map for the United States
Here is a zone-by-zone to-do list for Would perhaps. You’ll to seek out planting and garden care guidelines for bushes and shrubs, perennials, annuals, bulbs, the lawn, and container gardens on your house.
Use the USDA Hardiness Zone Map beneath to check your zone when you don’t seem to be positive.
Should you don’t seem to be positive when the remainder frost in spring happens where you might be residing–and when the main frost in autumn comes. Move to this publish: Average Last and First Frost Dates for Cities, States, and Countries. The months between the remainder frost in spring and the main frost in autumn is the natural emerging season on your house.
Zones 7-11: Warmth Space Vegetable Garden Would perhaps Checklist
If the weather has settled in your house, now might be the time to direct sow warm-weather vegetable seeds. Once the remainder frost is earlier, vegetable starts can go into the garden as effectively. Few seeds will germinate if the soil temperature is beneath 45ºF (7ºC) and warm-weather vegetation isn’t going to thrive until the night time time temperatures stay consistently above 50ºF (10ºC). Practice the high and low temperatures for a lot of days when you don’t seem to be positive if the time is correct to start out out sowing and planting out warm-season vegetation. If you happen to do get started and temperatures all of a sudden dip, use horticultural fleece or cloches to give protection to summer season veggies from danger. You are able to lower transplant marvel must you grab off hanging melons and summer season and winter squash seedlings inside the garden until 10 days after the date of the remainder expected frost. Peppers and eggplants may also be transplanted into the garden two to a couple of weeks after the remainder frost. Herb starts like dill, oregano, sweet marjoram, cilantro, rosemary, sage, and thyme may also be transplanted into the garden this month. Make certain the weather is settled warmth previous than you plant out basil and lemongrass.
If you happen to live in USDA Plant Hardiness Zones 7-11, here is a vegetable gardening checklist for Would perhaps: (In the United States, USDA Zones 10 and 9 include the Gulf Coast and parts of the South Atlantic states, the Pacific Southwest—mainly Southern California, and parts of the Barren area states. Temperature lows inside the coldest of the ones spaces can drop as low as 20°F (-7°C). In Europe, parts of Spain, Italy, and France and spaces of countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea are in Zones 10 and 9. USDA Zone 8 accommodates the Mid-South, Pacific Norwest states, and parts of Northern California. Zone 7 accommodates parts of the Northeast, Mid-Atlantic house, and eastern sections of the Northwest. Temperature lows inside the coldest of the ones spaces can drop as low as 0°F (-18°C). Numerous the United Kingdom, France, and parts of Spain are in Zone 8. The western spaces of Germany are in Zone 7.)
Greenhouse and cold frame Zones 7-11:
- Sow successions of mild vegetables paying homage to tomatoes, peppers, cucumbers, and runner beans to plant out later.
- Plant greenhouse tomato plants in massive pots, or plant them in increase baggage.
- Water and feed tomatoes, cucumbers, and peppers, under no circumstances letting the soil dry out. Remove aspect shoots from tomatoes.
- Attach slings or nets to greenhouse melons as they swell.
- Introduce natural controls to stick down pests paying homage to greenhouse whiteflies and spider mites.
Vegetables inside the garden Zones 7-11:
- Get began sowing vegetables without protection if the soil and nighttime temperatures have warmed.
- Thin beets, carrots, lettuce, radishes, spinach, and other half-hardy and hardy seedlings planted past due ultimate month. As vegetation are harvested, plant successions of early or get began introducing summer season vegetation.
- Early inside the month, get able outdoor web sites for cucumbers, squashes, and tomatoes. Erect is helping for runner beans, and place stakes, poles, and trellises in place for tall and mountain climbing vegetation.
- Stake tomatoes and tie them gently to stakes.
- Remove cloches from massive beans, carrots, and peas.
- Mid-month sowing: sow seeds of beans, lima beans, corn, okra, squash, cucumber, cantaloupe, Chinese language language cabbage, and other mild vegetables and herbs after temperatures have reached the 70sF.
- Sow cucumbers in mounds enriched with a lot of well-rotted manure and compost.
- Set out transplants after mid-month: tomato, eggplant, pepper, and sweet potato.
- Set out sweet potato slips on a cloudy day. Form a little of mound of soil over more youthful potato shoots to give protection to them from frost.
- Pinch out the tips about massive beans to encourage a excellent pod set and to deter an attack from aphids.
- Make further sowings of salad vegetation and summer season spinach.
- Save you watering onions, garlic, and shallots when the foliage begins to turn yellow.
Harvest early vegetation in Zones 7-11:
- Get began deciding on massive beans when the pods are finger thick.
- Continue to cut asparagus. Since the asparagus harvest ends, scale back female plants with berries.
- When peas stop producing, reduce vines to the ground (do not pull allowing their roots to fix nitrogen inside the soil). Change early cool-weather vegetation with summer season vegetation.
Succession plantings in Zones 7-11:
- Make successional sowings of early vegetation: beetroot, carrots, lettuces, and turnips. Make successive sowing of lettuce, salad vegetation, and summer season spinach, turnips, runner beans, green beans, endive, radishes, and kohlrabi.
Past due month sowing and transplants in Zones 7-11:
- Sow sweet corn out of doors in mild areas when further frost isn’t most probably. Most vegetables may also be sown now, so check out the packets.
- Sow French and runner beans, and pole beans, long-rooted beets, sea kale, salsify, and sweet corn.
- Plant out late-summer cauliflowers and inside the north Brussels sprouts. Plant out vegetable seedlings paying homage to cabbages, cauliflowers, celery, sweet corn, tomatoes, and marrows. Plant outdoor tomatoes, and tie them gently, on the other hand firmly, to stakes to protected them.
Herbs in Zones 7-11:
- Plant or pot up basil seedlings.
- Take cuttings of pot marjoram, rosemary, sage, and thyme.
- Divide and transplant perennial herbs.
- Divide any straggly mint and thyme plants.
- Plant or pot up basil seedlings.
Pests in Zones 7-11:
- Stay up for aphids on massive beans and root flies on cabbages, carrots, and onions. Keep after weeds.
Feeding and watering Zones 7-11:
- Give aspect dressing of compost tea to half-grown plants.
- Keep all plants watered and effectively mulched.
Fruit bushes in Zones 7-11:
- Feed summer-fruiting plants with potassium sulfate to promote it excellent flowering and fruit. Control weeds spherical bush and cane fruit.
- Thin the fruit on apples, peaches, nectarines pears, and plums when they achieve marble-size. Thin heavy-cropping nectarines and peaches when the fruit is ½ in (1-1.5 cm) in diameter.
- Water new plantings deeply if the weather is dry. Water plentifully when the fruit is swelling.
- Clutch codling moth traps on apple bushes.
- Spray against apple scab, mold, and aphids.
- Prune wood damaged thru hearth blight.
- Remove any shoots on well-trained end result which can be emerging directly in opposition to or transparent of the wall.
- Remove the blossoms from newly planted fruit bushes to direct the plant’s energy into the producing of strong new wood.
Berries in Zones 7-11:
- Plant new strawberries and put cloches over strawberries if you wish to have an early corp. Harvest strawberries as they ripen. Protect strawberry end result with straw or black plastic sheeting.
- Keep new canes of blackberries and loganberries break free the existing 365 days’s fruiting canes. Tie new canes of blackberries and hybrid berries to a machine of toughen wires, allowing a maximum of 8 canes in line with plant.
- Remove inclined shoots from brambles. Thin our raspberry canes. Spray raspberries against raspberry beetles. Follow the main spray as soon as the main fruit turns purple.
- Summer time-prune gooseberries thru reducing once more aspect shoots to five leaves.
- Feed blackberry and hybrid berry plants with ammonium sulfate or other high-nitrogen fertilizer. Quilt berries with netting to give protection to them from birds.
Citrus in Zones 7-11:
- Plant citrus and tropical fruit this month. Feed citrus fruit with sulfate of ammonia; feed established bushes with iron sulfate. Water citrus deeply in dry local weather.
Containers in Zones 7-11:
- Plant summer season container plants when the danger of frost is earlier.
- Feed new transplants with liquid fertilizer and water as sought after.
Zones 3-6: Cool Space Vegetable Garden Would perhaps Checklist:
In cool- and cold-winter spaces, the danger of freezing local weather and frost continues through Would perhaps in USDA Plant Hardiness Zones 6, 5, 4, and 3. Here is a checklist of things to do inside the vegetable garden in cool and cold spaces all over April inside the Northern Hemisphere: (USDA Zones 6, 5, 4, and 3 are one of the northern and coldest winter spaces of the United States the northern parts of the Rocky Mountains, northern Plains and the Midwest States, and the northern spaces of the Northeast and into Canada. Temperature lows inside the coldest of the ones spaces can drop as low as -40°F (-40°C). Jap Europe is largely in Zone 6 and Zone 5.) The weather in cool northern spaces can keep unsettled even in Would perhaps.
Understand that each and every the soil and air temperatures are crucial when planting the kitchen garden. Few seeds will germinate if the soil temperature is beneath 45ºF (7ºC), and warm-weather vegetation don’t seem to be going to thrive until the night time time temperatures consistently stay above 50ºF. By means of the highest of the month–or two to a couple of weeks after your ultimate frost, your kitchen garden will be capable to welcome cucumbers, bush and pole beans, and tomatoes. Throughout the length in-between, you can get the ones vegetation entering into a greenhouse or cold frame or inside the kitchen window. If you happen to get the seedlings emerging now, you’ll experience an earlier harvest next summer season. Strawberries may also be planted now. June-bearing-type strawberries are energetic and spread runners rapidly and should be producing in June. Everbearing-type strawberries will fruit in June and over again later inside the fall. If you are on the lookout for the perfect to increase, check out Alpine strawberries. Peas. Cool-weather vegetation paying homage to peas should be in a position for harvest later this month or in June previous than the weather warms. Keep your eye on cauliflower and Brussels sprouts to get them out of the garden at their peak and previous than they bolt in warmth local weather.
Greenhouse and cold frame in Zones 3-6:
- Open the greenhouse and cold frame for warm rain and sun; close them if the temperature drops to near freezing.
- Early inside the month, sow underneath quilt half-hardy annual seeds: tomato, eggplant, pepper, and runner beans. Plant greenhouse tomato plants and cucumbers in massive pots or increase baggage.
- Harden off vegetable starts inside the cold frame for 10 days previous than setting them out. By means of the middle of the month, you can harden off tomato plants and in a position them for setting out past due inside the month.
- Harvest asparagus and other early vegetation from the cold frame.
- Introduce natural controls to stick down pests paying homage to greenhouse whiteflies and spider mites.
Vegetables early inside the month Zones 3-6:
- As soon as the ground may also be worked, add soil amendments, humus, and manure to the planting beds if the ones were not added inside the fall. Get able beds for planting and sowing.
- Warmth up the soil in cool spaces with cloches or black plastic.
- When the danger of heavy frost is earlier, sow or plant out cool-weather vegetation; harden off more youthful plants from winter sowings of broccoli, cabbage, cauliflower, leeks, onions, lettuce, peas, and large beans previous than planting out.
- Get began sowing vegetables without protection must you might be residing in mild spaces. Many seeds may also be sown from early spring onwards. Check out seed packets as some types are further suitable than others for early sowing.
- Direct seed massive beans, broccoli, Brussels sprouts, cabbage, carrots, cauliflower, kohlrabi, leeks, lettuce, onions, parsnips, peas, radishes, and spinach.
- Plant asparagus, rhubarb, and celery. Dig well-rotted manure into celery trenches.
- Get able runner-bean trenches thru digging in compost or well-rotted manure.
- Plant early potatoes and onion devices.
- Use horticultural fleece or cloches for early vegetation.
- Thin out overcrowded vegetable seedlings sown earlier: thin beets, carrots, lettuce, radishes, and spinach.
- Mulch after the soil has warmed and plants are a lot of inches over the top.
- Put is helping in place for peas.
- Turn the compost pile.
- Protect vegetable starts from drying winds and keep them effectively watered.
- Colour transplants from direct sun for every week or until re-established out of doors.
- Weed and water as sought after.
- Stay up for insects and signs of sickness.
Succession planting cool-weather vegetation in Zones 3-6:
- Make second sowing of early peas and other vegetation as the main harvest is to be had in.
- Feed lettuce and other early vegetation with compost.
Vegetable planting after mid-month in Zones 3-6:
- Plant warm-weather vegetation and delicate herbs when the danger of frost is earlier and the soil has warmed up and the weather settled. Sow seeds of beans, corn, okra, squash, cucumber, cantaloupe–all mild vegetables–when the weather has warmed into the 70s.
- Set out plants of tomato, eggplant, pepper, and sweet potato.
End result and berries in Zones 3-6:
- Plant fruit bushes and brambles when soil workable. Paint white or wrap trunks of more youthful bushes to forestall sunscald.
- Water new plantings deeply if the weather is dry.
- Feed summer-fruiting plants with potassium sulfate to promote it excellent flowering and fruit.
- Plant new strawberries, and place cloches over strawberries if you wish to have an early cop. You’ll want to quilt strawberries if a past due frost is conceivable.
- Plant currant bushes and raspberry canes, and water them in completely. Decrease the canes down to 12 inches above the ground.
- Thin brambles (blackberries, raspberries, loganberries); prune away inclined shoots. Prune once more the stems of newly planted and two-year-old gooseberries thru about one-half. Spray gooseberries and black currants for gooseberry mold.
- Fertilize or top-dress with compost established berries and grapes if not accomplished ultimate month. Feed blackberry and hybrid berry plants with ammonium sulfate. Control weeds spherical bush and cane fruit.
- If fruit bushes are nevertheless dormant apply a dormant spray to apples, pears, and plums.
- Thin the fruit on apples, pears, and plums when marble-size. Thin heavy-cropping nectarines and peaches when the fruit is ½ inch (1-1.5 cm) in diameter.
- Change mulches removed ultimate month.
- Prune suckers and water sprouts from bushes.
- Stay up for pests and signs of sickness. Trap larvae on trunks of bushes and spoil them.
Containers in Zones 3-6:
- When frost danger is earlier, switch boxes out of doors over again.
- Plant cool-weather and later warm-weather vegetables in boxes when the danger of frost is earlier. Feed new plants with liquid fertilizer.